CCG Releases New Report on State Participation in Global Governance
June 05 , 2019
A new report entitled “2016 States’ Participation Index of Global Governance World Report” was released on Sept. 22 at CCG. This report is a joint effort by Center for China and Globalization, Political Science Institute of East China University of Political Science and Law, and Center for International Communications Studies at China International Publishing Group. It evaluates the participation and contribution of 189 countries in the world in global governance, indicating four of the top five countries on the ranking list are the permanent members of the UN Security Council. Integrating the common acknowledgement of the latest G20 summit in Hangzhou, the report also proposes Chinese perspectives in global governance reform to push forward its development and innovation.
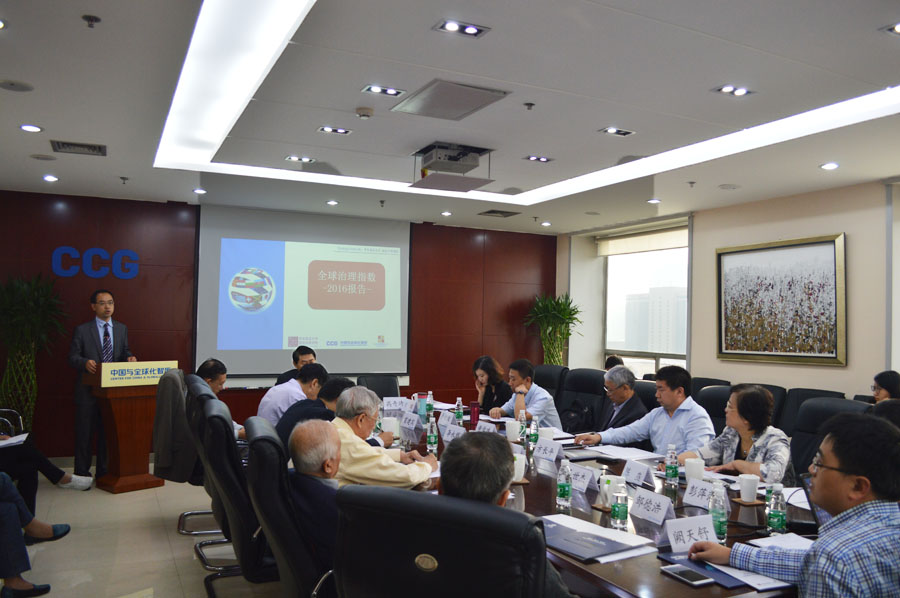

The project was initially launched in 2014 with a focus on 25 major economies, including G20, in the annual reports for 2014 and 2015. This year, the research team has further modified some indicators and expanded the evaluation to a total number of 189 countries.

CCG President Wang Huiyao said at the releasing news conference that as a result of globalization, a number of global issues such as economy, investment, finance, migration and development cooperation require world solution. Therefore, the study of the system in which states can participate in global governance is highly important and constructive.
The evaluation is based on four primary indicators – mechanism, performance, decision-making and responsibility in order to evaluate the participation and contribution in global governance and 24 secondary indicators. Based on the information collected from UN organizations, media reports and self-generated data, among all the countries evaluated, the top five most participating and contributing countries in global governance are the United States, France, United Kingdom, China and Japan. Russia is ranked No. 6, followed by Germany, Canada, Italy and India. In a sharp contrast with those major economic powers, many countries in Africa, Middle East, Central Asia and Pacific and Caribbean score lower than average.
The report also finds that emerging powers such as China, India and Brazil are becoming more increasingly important forces in global governance. China, for an instance, scores high for its big contribution to world economic growth and great performance in global governance on economic affairs. Mainly due to the large number of personnel India has sent to UN peacekeeping troops, it scores high in global governance responsibilities. A few developing and underdeveloped countries’ scores high in some specific indicators because of their good performance in poverty reduction and public health.
Given the fact that the world political and economic landscape has undergone dramatic change and a wave of de-globalization is spreading in some countries. Isolationism and nationalism are gradually rising. At the same time, emerging economies are playing an increasingly important role in world affairs, has becoming a propelling force for reform. The report calls for joint efforts to establish a more representative and effective mechanism for global governance from all countries.
Based on the evaluation results of the SPIGG project, the report proposes the theme of “China’s plan and the future for global governance”
The short-term plan by 2020 will focus on promoting the sustainable growth of the global economy, reinforcing G20 and other multilateral organization’s role and impact, and facilitating China’s provision of public products and services to the rest of the world. The mid-term plan for 2030 will be aimed at promoting the inclusive growth of the global economy, and supporting the emerging countries to participate in global governance and provide more public products and services to the world. In the long-term by 2050, the efforts should focus on promoting the reform of the UN, building up the UN’s influence in global governance, and establishing a perfect mechanism of global governance.

Gao Qiqi, Director of the Political Science Institute at East China University of Political Science and Law, concluded that the 2016 ranking report covering 189 countries is more authoritative and with more depth and breadth, can hopefully encourage and incentivize each state to participate in global governance and improve the mechanism together to overcome the challenges.